CBD vs THC – Why One Makes You High & The Other Does Not
As the cannabis industry is growing at an incredible rate, you might have heard about THC and CBD. Among hundreds of cannabinoids (chemical compounds found in the cannabis plant), THC and CBD are the most familiar and widespread ones.
Most people know that THC will make you high, whereas CBD won’t. But this is the small part of the whole story.
Cannabinoids, found in cannabis plant, interact with our bodies in sophisticated and unique ways. If you dig deeper into the science behind these two cannabinoids, it will become apparent that there is more to learn about THC and CBD.
THC is The Most Popular Compound of The Cannabis Plants
Among the many intoxicating substances on earth, THC from the cannabis plant is the safest one. We still clearly don’t know how cannabis creates intoxication in our body when compared with other drugs, however, we do know the following about cannabis.
Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the main intoxicating element in the cannabis, which was first described in the 1940s. Israeli scientist Rafael Mechoulam synthesized this molecule in 1965 and our understanding of THC has improved ever since.
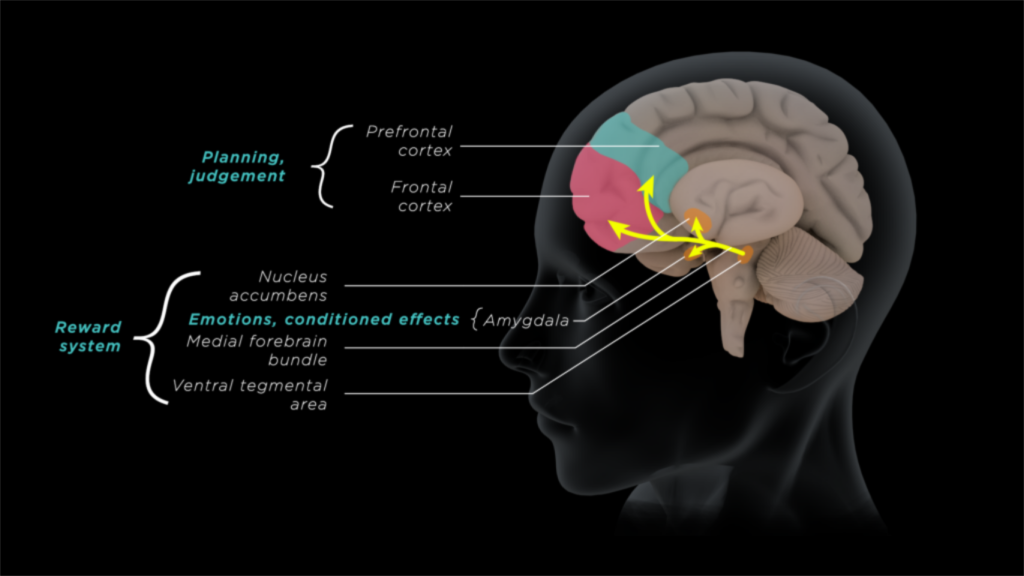
We have CB1 receptors throughout our body and THC acts as an activator or agonist of these CB1 receptors. But if people with blocked CB1 receptors are given cannabis (by a different drug, called an antagonist), it won’t make them high. So now we know that to produce intoxication by THC, CB1 receptors in our brain play a crucial role.
It is known from brain imaging studies during THC intoxication process that blood flow to the prefrontal cortex region of the brain increases. This prefrontal cortex region is responsible for attention, decision making and other executive functions, like motor skills. Any of these functions can be affected by THC intoxication to varying degrees, depending on each person’s response to the THC.
Cannabis intoxication also plays a vital role in our brain’s rewards circuitry, which caters our memory process and emotional wellbeing. Activity in this region of brain creates a sensation of happiness and regulates emotion that ultimately controls our behavior. It is the very same trigger that drives us to as ask a potential mate out on another date or to revisit that greasy burger place for a meal when we know it is high in calories.
The use of THC from cannabis make us feel good, as it activates the brain’s reward system, and it is likely that one will give it a try. THC’s ability to create euphoric effects come from its ability to bind with the CB1 receptors in our brain’s reward system.
“CBD Does Not Get You High” But That Is Not The End Of The Story
THC is not the only compound found in Cannabis plant that has a direct impact on the functions of our brain. The second most important cannabinoids found in the Cannabis plant is Cannabidiol or CBD. CBD is called a non-psychoactive. CBD has very powerful properties that can reduce anxious feelings and it interacts with the receptors of our brain.
CBD is also not intoxicating. When it comes to activating the CB1 receptor, CBD is not as good as THC and this property makes it non-intoxicating. Evidence suggests that in presence of THC, CBD interferes with the activity of CB1 receptor. Users feel a nuanced subjective high and have less chance of experiencing paranoia when THC and CBD work together with the CB1 receptor. It is because CBD inhibits the CB1 receptor, while THC activates it. The presence of two cannabinoids balances the effects.
When other cannabinoid and terpene molecules are consumed alongside CBD and THC, things get even more interesting. We are in the very beginning stages of understanding the isolated effects of cannabinoids’ (i.e. CBN, CBC, CBG) ability to bind to targets in the brain. They could potentially prolong, interfere with, enhance or in some other ways modify the effects of THC. It is possible that, some most well known effects (i.e. couch lock) of cannabis, may have very little to do with THC itself.
The cannabis plant is complex and we have little available research on its effects and interactions with human body. We are in the beginning stages of learning how the many compounds in cannabis work together with our body and change the way we feel.
